This article is for informational purposes only. It may contain graphic images, reader discretion is advised.
A proper trauma assessment is the cornerstone to any EMT’s skill set. DCAP BTLS is an easy to remember acronym that helps emergency first responders perform a rapid and detailed assessment.
What is DCAP BTLS?
DCAP BTLS stands for Deformities, Contusions, Abrasions, Punctures/Perforations, Burns, Tenderness, Lacerations, and Swelling. These are the main clues a responder will look for when assessing a trauma patient. Some of these can even apply to medical emergencies. Below we detail what each condition is and what to look for.
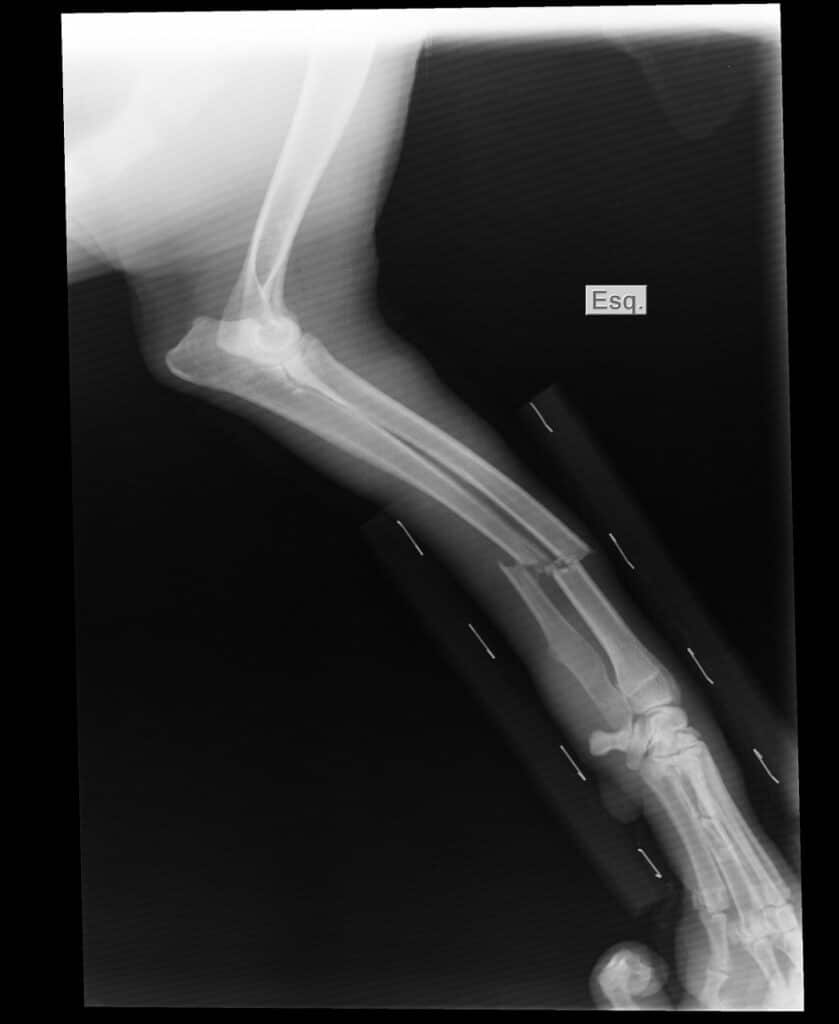
Deformities
Contusions
Contusions are bruising. This is a collection of blood under the skin. Contusions are usually an indication of blunt trauma. When bruises are present then your index of suspicion should be high for underlying injuries.
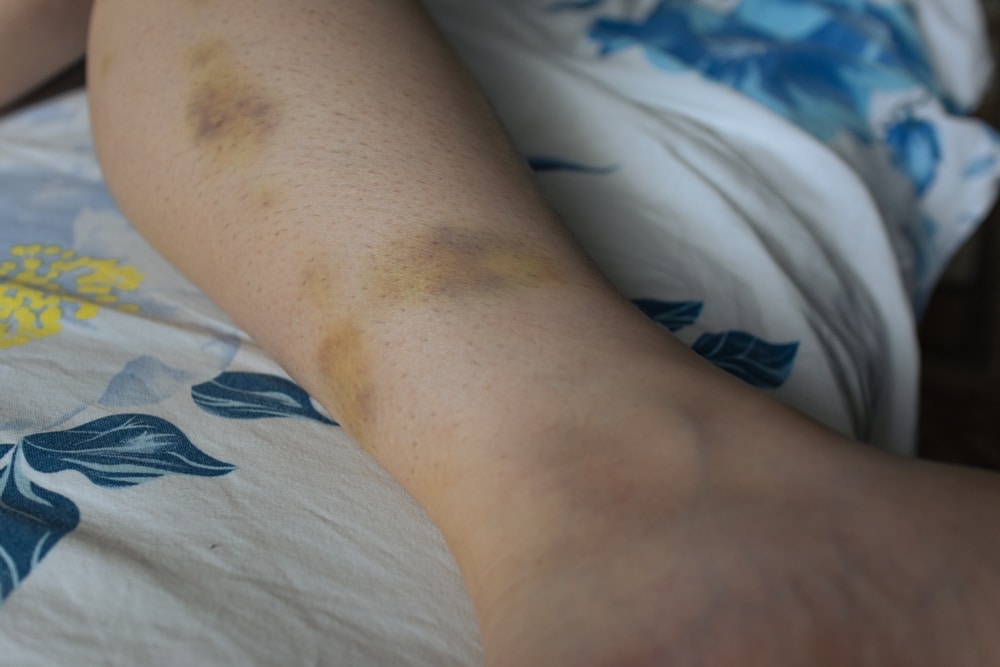
For example, you have a patient that was involved in an assault. He has contusions to his upper left abdomen. Your patient might appear to be fine, but the contusion could indicate damage to his spleen.
Abrasions
Abrasions are loss or damage of the top layer of the skin. Abrasions are characterized by redness and minor bleeding. If you ever scrapped your knee as a kid then you had an abrasion.
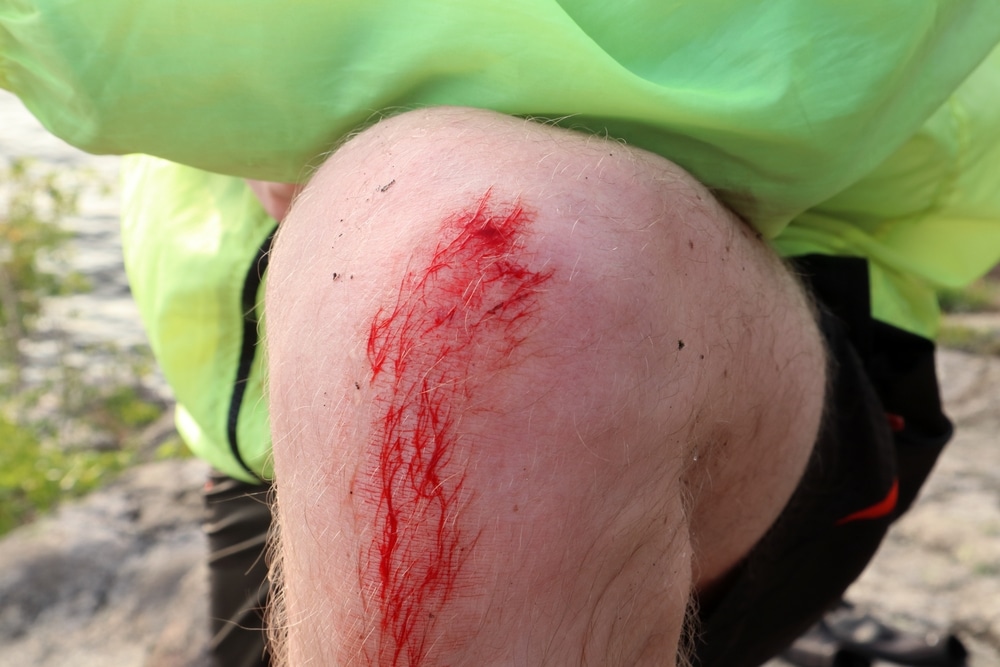

In a motor vehicle accident, this can be known as a road rash. Since the skin has been violated, an abrasion is considered an open injury.
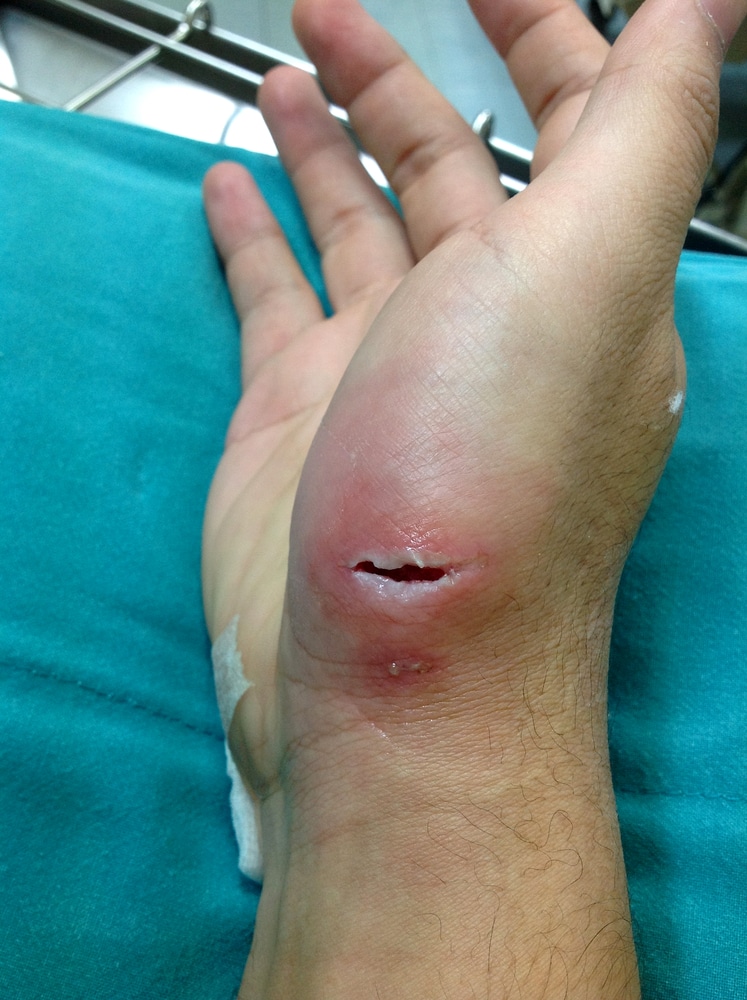
Punctures and Penetrations
Burns
Burns happen when the skin is not able to withstand the energy enacted upon it. Burns can be caused by extremely high and extremely low temperatures. Burns are also caused by chemical exposure to acids and bases.

Thermal burns are typically classified into three stages. Superficial (1st degree) burns affect the top layer of the skin, think of a sunburn.

Partial Thickness Burn
Axelv, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Partial thickness (2nd degree) are burns that affect the skin at the dermal layer. These burns usually come with extreme pain and blisters.
Finally, full thickness (3rd degree) burns affect all layers of the skin. Typically, these burns have no pain at the sight due to the fact that the nerve endings have been destroyed. The skin resembles cooked chicken or pork.

Chemical burns are typically superficial and can cause rash, discoloration of the skin, or even peeling of the layers.
Electrical burns usually have an entrance and exit wound and can be superficial (as in lightning strikes) or full thickness.
Tenderness
Tenderness is pain at a site that appears upon palpation. For example a patient has a broken limb and it hurts when pressure is applied.
Not all tenderness presents with pain when palpated. Rebound tenderness happens when the area is pressed upon. The pain happens when the pressure is released. This is a sign of an appendicitis then present in a patient complaining of right lower quadrant abdominal pain.
Lacerations
Lacerations are deep cuts. If you have ever cut yourself on a knife or piece of glass then you have had a laceration.
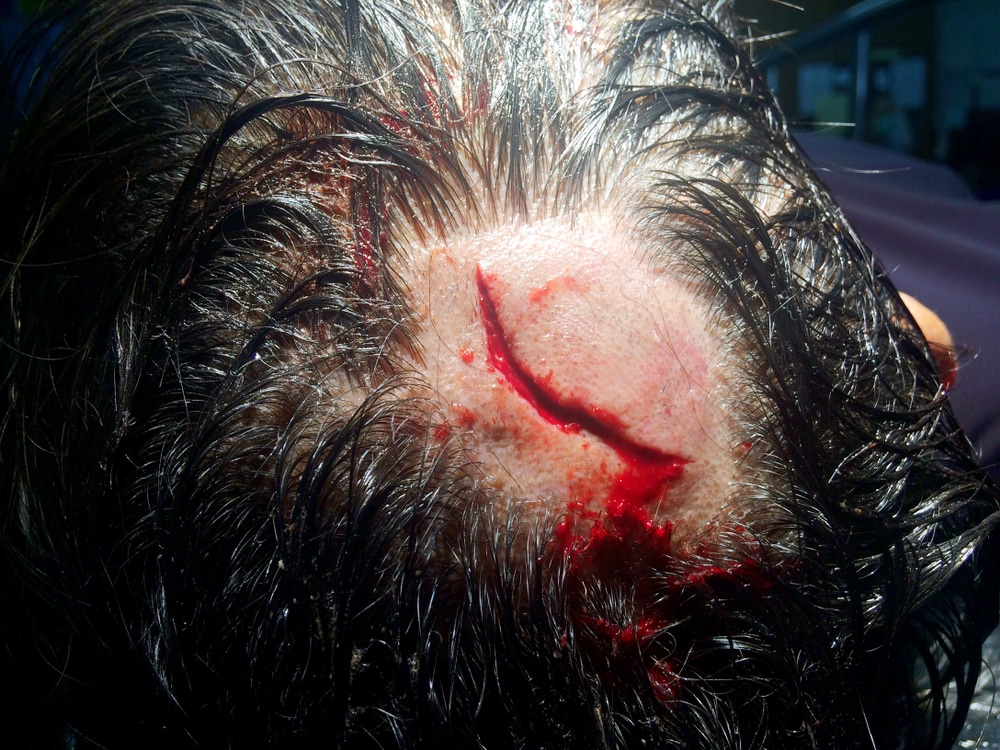
Lacerations are particularly dangerous because of the area that a laceration can cover. With lacerations there is increased chances for traumatic bleeding.
Incisions are a type of laceration. Incisions tend to be purposeful and precise. For example, a patient has had recent surgery. The surgery sight will most likely contain an incision.
Swelling
Swelling happens when there is fluid build up under the skin. Swelling can have traumatic and non traumatic causes.

What is DCAP BTLS used to assess?
DCAP BTLS is primarily used for the assessment of a patient that has suffered traumatic injury. However, there are times when using DCAP BTLS is part of a medical assessment as well.
Anytime you have a patient complaining of pain you can use this acronym along with OPQRST to assess and provide care for your patient.